All Basic Information About What is Sintering ?

What is Sintering ?
Simple to Say, Sintering is a heat treatment process used to transform powdered materials into a solid mass, without reaching the point of complete melting.
This transformation occurs by heating the material below its melting point until its particles adhere to each other. Sintering is widely used in various industries such as metallurgy, ceramics, and even 3D printing to produce dense and robust materials from powders.
But did you know that the concept of sintering is not a modern invention?
In fact, its origins can be traced back to around 3000 BC, when it was used for making ceramic objects. The modern scientific understanding and widespread industrial use of sintering, however, have developed mainly over the last century.
As you can imagine, sintering plays a crucial role in a plethora of applications. From making spark plugs, ceramic capacitors, and dental crowns to constructing high-tech industrial components, sintering has proven to be indispensable.
Different Types of Sintering
Now that you know what sintering is and how it's been used throughout history, it's time to introduce you to the different types of sintering. Yes, there's more than one way to sinter!
First up is solid-state sintering. This type is the most basic and common form of sintering. Here, the powdered material is heated until the particles begin to bond together. It’s like how you might build a sandcastle – the grains of sand stick together, but they don’t melt.
Next, we have liquid phase sintering. This type involves a mixture of two or more materials. The mixture is heated to a point where one of the materials melts and forms a liquid phase, which helps in bonding the remaining solid particles together.
Third on the list is activated sintering. In this case, an additive or a catalyst is used to speed up the sintering process. Think of it as adding yeast to dough – it makes the bread rise faster.
Lastly, there are pressure-assisted sintering techniques like hot pressing and spark plasma sintering. As the name suggests, these techniques use pressure in combination with heat to speed up the sintering process and produce denser materials.
Each type of sintering has its own set of advantages and is used for specific applications. The choice depends on factors such as the material being used, the desired properties of the final product, and the available equipment. In the upcoming sections, we'll delve deeper into specific sintered materials and the sintering process itself.
Stay tuned for more fascinating insights into the world of sintering!
Exploring Sintered Materials
Then Next we need to understand the different types of sintered materials.
I'm sure by now, you're getting the hang of the sintering process. But what about the products of this intriguing process?
One of the most commonly produced materials is sintered metal. The process involves compacting and forming metal powder under heat, turning it into solid metal. The result is a metal with a high degree of purity and uniformity. Sintered metal can be found in a variety of industries, from automotive components to medical implants, due to its robustness and versatility.
Next, let's talk about sintered stone. Sintered stone is produced by applying heat and pressure to natural minerals, clay, and feldspar, creating a nearly indestructible material. You'll often find sintered stone in high-traffic areas like kitchen countertops or bathroom tiles, where durability is key.
Sintering also plays a pivotal role in ceramics. The process enables us to mold ceramics into a multitude of shapes with complex geometries that wouldn't be possible with traditional methods. From ceramic tiles to pottery, sintering has had a transformative impact on this sector.
Lastly, there are various other special sintered materials to explore. These range from composite materials, like metal-ceramic composites, to functionally graded materials, where the composition varies across the component.
Sintering Process Explained
Let's move on from products to the process itself. How does sintering happen, and what are the key stages involved?
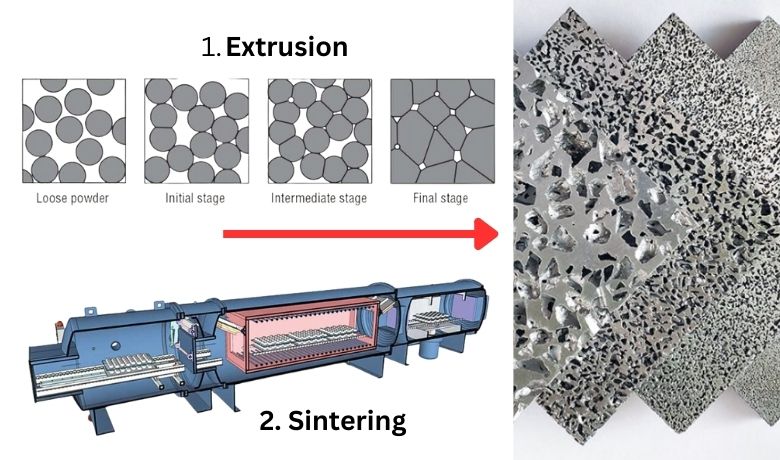
To start with, the pre-sintering steps are crucial. The raw material, whether it be metal, ceramic, or otherwise, must be prepared in powder form. This powder is then shaped into the desired form, often through a process called 'green compacting'.
Next comes the heart of the operation: the sintering process. The shaped powder is heated in a controlled environment, usually a furnace, to a temperature just below its melting point. This allows the particles to bond together without fully melting, forming a solid mass.
Once the sintering process is complete, the material enters the cooling phase. This needs to be managed carefully, as rapid cooling could lead to cracking or other structural issues. Cooling slowly allows the material to settle and solidify effectively.
Lastly, we cannot forget the factors impacting sintering, specifically, temperature and time. The sintering temperature needs to be high enough to facilitate bonding but low enough to prevent full melting. Similarly, the time the material spends in the sintering process can greatly impact the final product's properties.
In the next part of our sintering saga, we will dive deeper into sintered filters and uncover the conditions required for sintering. So stay tuned!
Sintered Filters: An Application Spotlight
We've already covered the basics of sintering, explored a variety of sintered materials, and discussed the sintering process in detail.
Now, let's focus on a specific application of sintering filters.
Perhaps one of the most noteworthy applications of sintering is in the creation of sintered metal filters. These filters are produced from metal powders, compacted and sintered to create a porous but strong filter medium. The pore size of these filters can be precisely controlled, providing superior filtration capabilities in comparison to traditional woven wire mesh filters.
You may wonder, why use sintered metal filters? The answer lies in their durability and resistance to high temperatures and pressures. These properties make sintered metal filters indispensable in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to petrochemicals and food and beverage production.
Another fascinating application of sintering in filtration is the sintered glass filter. These are made by fusing together tiny glass particles at high temperatures. They're often used in laboratories for filtration and gas distribution because of their high chemical resistance and precise pore size.
Sintered filters, be it metal or glass, exemplify the capabilities of sintering in creating superior materials with distinct advantages.
Understanding Sintering Conditions
Now, let's turn our attention to the sintering conditions. When we talk about the sintering process, the conditions under which it takes place are of utmost importance.
Firstly, the sintering temperature plays a pivotal role in the process. It needs to be just below the melting point of the material, to allow particles to bond without fully melting. It's a delicate balance that can greatly impact the final product's quality.
Then there's the matter of gas. You might be wondering, "What gas is used in sintering?" Typically, sintering is carried out in a controlled atmosphere to prevent undesirable reactions between the material and the surrounding gases. Often, inert gases like nitrogen or argon are used, although the specific choice depends on the material being sintered.
Pressure also comes into play, especially in pressure-assisted sintering techniques. Higher pressure can result in denser materials, as particles are forced closer together.
Finally, the material properties and equipment used are significant factors. Different materials react differently to heat and pressure, requiring varying conditions for optimal sintering. The type of furnace or sintering machine can also influence the process, as we'll discuss in the next section.
Stay tuned as we explore more about sintering machines and their role in the sintering process!
Sintering Equipment: A Look at Sintering Machines
Up until now, we've been thoroughly exploring the concept of sintering, sintered materials, and the process itself.
Now let's shine a spotlight on the main player behind the scenes: the sintering machine.
A sintering machine is the cornerstone of the sintering process. But what exactly is a sintering machine? Essentially, it's a specialized furnace designed to carry out the sintering process under carefully controlled conditions.
There are various types of sintering machines available, each suited for different materials and sintering methods.
1. These include Continuous sintering machines (used in industries that require high-volume production),
2. Batch sintering machines (more common in labs or for low-volume production), and
3. Vacuum sintering machines (which allow sintering in a vacuum or controlled atmosphere).
The way a sintering machine works is straightforward yet fascinating. It uniformly heats the powdered material to a specific temperature, maintains this temperature for a predetermined period, and then cools the material slowly, all while ensuring the atmosphere within is controlled.
Choosing the right sintering machine is crucial and depends on several factors, including the material to be sintered, the desired throughput, and the specific sintering conditions required.
The Significance and Future of Sintering
Now it's time to reflect on the bigger picture: What is sintering used for, and why is it significant?
The applications of sintering are vast and varied. It's used to create dense, durable products with complex geometries, from industrial components to consumer goods. Sintering allows us to produce high-quality materials, like sintered metal and sintered filters, with unique properties such as controlled pore size and improved durability.
But what does the future of sintering look like? Emerging trends suggest an increase in the use of pressure-assisted sintering techniques for producing advanced materials. The development of more efficient sintering machines and the use of sintering in additive manufacturing (3D printing) are other promising trends.
Despite these advancements, sintering also faces challenges, such as achieving greater control over the process and reducing energy consumption. Addressing these will be key to unlocking the full potential of sintering in the future.
Conclusion: Sintering, while a complex process, holds a significant impact on various industries. Its ability to transform simple powders into robust, complex materials makes it an invaluable process. As we look forward to the future, the evolution and refinement of sintering promise exciting opportunities for new materials and applications.
FAQ
1. What is the sintering process?
Sintering is a heat treatment process that transforms powdered materials into a solid mass without melting the material completely. It involves heating the powdered material below its melting point until the particles begin to adhere to each other, forming a solid mass. This process is used in various industries such as metallurgy, ceramics, and additive manufacturing to produce dense and robust materials from powders.
2. How does sintering work?
The sintering process involves three main stages: heating, holding, and cooling. The powdered material is first compacted and formed into the desired shape, then heated in a controlled environment to a temperature just below its melting point. The heat causes the particles to bond together, forming a solid mass. After maintaining this temperature for a predetermined period, the material is then cooled slowly to prevent cracking or other structural issues.
3. What materials can be sintered?
A wide range of materials can be sintered, including metals, ceramics, plastics, and glass. Different materials require different sintering conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and atmosphere. Some materials can be directly sintered, while others require additives or binders to facilitate the process.
4. What is a sintered filter, and why is it used?
A sintered filter is a type of filter produced through the sintering process. It can be made from metal, ceramic, or glass powders, compacted and heated until the particles bond together. The pore size of these filters can be precisely controlled, providing superior filtration capabilities compared to traditional filters. Sintered filters are highly durable and resistant to high temperatures and pressures, making them useful in various industries like pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and food and beverage production.
5. How is sintering used in additive manufacturing (3D printing)?
In additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, sintering is used in methods like selective laser sintering (SLS) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). These methods involve using a laser to sinter powdered material layer by layer, building up the desired 3D object. The ability to control the sintering process precisely makes it possible to produce complex shapes and geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
6. What is the future of sintering?
The future of sintering looks promising, with advancements in technology opening up new possibilities. For example, pressure-assisted sintering techniques are becoming increasingly popular for producing advanced materials. The development of more efficient and precise sintering machines, and the use of sintering in additive manufacturing, are other promising trends. However, challenges such as achieving greater control over the process and reducing energy consumption need to be addressed to fully unlock the potential of sintering.
Whether you're looking to implement sintering processes in your operations or seeking high-quality sintered materials for your projects, HENGKO is here to assist. Our team of experts stands ready to provide advice, solutions, and services tailored to your unique needs.
Don't hesitate to reach out to us for more insights into the fascinating process of sintering or to explore our wide range of products and services. Simply drop us an email at ka@hengko.com, and we'll be in touch soon. we're committed to helping you turn powdered possibilities into solid success!
Send your message to us: