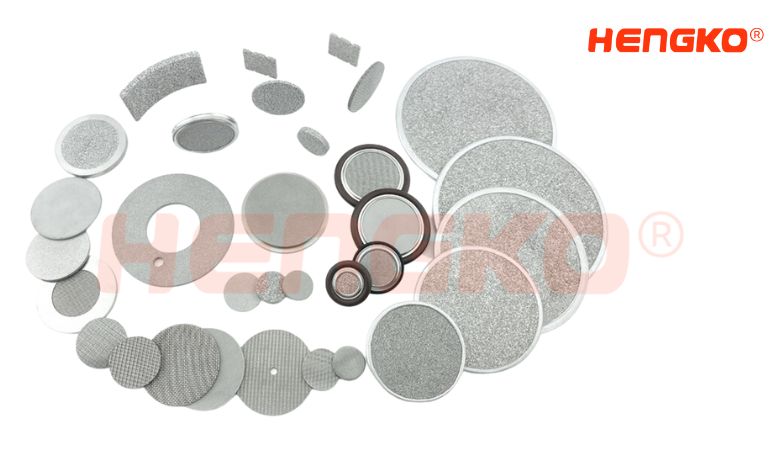
Beyond Filtration Porous Metal Discs The Unsung Heroes of Industry
You’ll find porous metal discs to be a game-changer across various industries, thanks to their interconnected pore structure. Made from different metals, these discs offer a unique blend of properties that make them essential for a wide range of applications. Whether you need superior filtration, efficient fluid distribution, or precise gas diffusion, these discs deliver exceptional performance while maintaining outstanding durability and stability, even in extreme conditions.
Porous Metal Discs: A Glimpse into Their Versatility
You can fabricate porous metal discs using various techniques, including sintering, etching, and electrospinning. These methods give you precise control over pore size and distribution, allowing you to tailor the disc’s properties to meet specific application needs. With porosity levels ranging from 30% to 90%, you can adjust permeability to optimize filtration, fluid distribution, and gas diffusion for your particular requirements.
Comparative Analysis: Porous Metal Discs versus Traditional Materials
To truly appreciate the significance of porous metal discs, let's compare them with traditional materials used in various industries.
Filtration
In the realm of filtration, porous metal discs stand out for their superior efficiency and durability. Their intricate pore structure traps contaminants with remarkable precision, even at the submicron level. Additionally, their resistance to corrosion and high temperatures makes them ideal for harsh environments. Compared to paper or polymer filters, porous metal discs offer significantly longer lifespans and reduced maintenance costs.
Fluid Distribution
Porous metal discs excel in fluid distribution applications, ensuring uniform flow and preventing channeling. Their controlled pore geometry allows for precise control over flow rate and pressure distribution. This makes them ideal for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace, where consistent fluid delivery is crucial. Traditional materials like perforated plates or wire meshes often struggle to achieve the same level of precision and consistency.
Gas Diffusion
Porous metal discs play a pivotal role in gas diffusion applications, facilitating efficient gas exchange and promoting chemical reactions. Their high porosity and interconnected pore structure minimize diffusion resistance, allowing gases to permeate through the disc rapidly. This makes them essential components in fuel cells, batteries, and gas sensors, where gas diffusion efficiency is paramount. Traditional materials like porous ceramics or polymer films often exhibit lower gas permeabilities and limited stability under high pressure or temperature conditions.
Conclusion: Porous Metal Discs – A Material of the Future
Porous metal discs have firmly established themselves as a material of significance, revolutionizing various industries with their unique combination of properties. Their superior filtration capabilities, exceptional fluid distribution, and efficient gas diffusion make them indispensable for a wide range of applications. As technology advances and new applications emerge, porous metal discs are poised to play an even more crucial role in shaping the future of engineering and manufacturing.
1. Understanding Porous Metal Discs
1.1 Description of Porous Metal Discs
Porous metal discs are a class of engineered materials characterized by their interconnected network of pores. These pores, ranging in size from micrometers to millimeters, allow for the controlled passage of fluids and gases while effectively filtering out contaminants. Porous metal discs are typically manufactured from metals such as stainless steel, bronze, and nickel, offering a combination of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
1.2 Manufacturing Processes of Porous Metal Discs
Several techniques are employed to fabricate porous metal discs, each with its own advantages and limitations. Common manufacturing methods include:
1. Sintering: Sintering involves compressing metal powder into the desired shape and then heating it to a temperature below the melting point. This process allows the metal particles to bond together, creating a porous structure.
2. Etching: Etching involves selectively removing material from a solid metal substrate to create pores. This method offers precise control over pore size and distribution.
3. Electrospinning: Electrospinning utilizes an electric field to draw fine fibers from a polymer solution. These fibers can be sintered or bonded together to form a porous metal disc.
1.3 Advantages of Porous Metal Discs
Porous metal discs offer several advantages over traditional materials such as paper, polymer, or ceramic filters:
1. Superior Filtration Efficiency: Porous metal discs can effectively filter contaminants at very small sizes, down to submicron levels.
3. Reusability and Sustainability: Porous metal discs can be cleaned and reused multiple times, reducing environmental impact.
4. Versatility and Customization: Porous metal discs can be customized in terms of pore size, porosity, and material composition to suit specific applications.
5. Biocompatibility: Certain porous metal discs are biocompatible, making them suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications.
2. How many Types of Porous Metal Discs ?
Porous metal discs are classified according to their pore size, porosity, and material composition.
Here are some of the most common types:
1. Sintered Porous Metal Discs:
These discs are made by sintering metal powder at a high temperature.
The resulting discs have a uniform pore size and distribution, making them
ideal for filtration applications.
2. Etched Porous Metal Discs:
These discs are made by etching a pattern into a solid metal sheet.
This method allows for precise control over pore size and shape,
making them suitable for applications
where high precision is required.
3. Electrospun Porous Metal Discs:
These discs are made by electrospinning a solution of metal nanoparticles onto a substrate.
The resulting discs have a very high porosity and a random pore structure, making them suitable
for applications where gas diffusion is important.
4. Graded Porous Metal Discs:
These discs have a gradient of pore size from the surface to the interior.
This gradient allows for more efficient filtration, as larger particles are trapped
on the outer surface
and smaller particles are trapped on the inner surface.
5. Multilayer Porous Metal Discs:
These discs are made by layering several discs of different pore sizes together.
This allows for the creation of complex filtration systems that can remove a wide
range of contaminants.
6. Wicking Porous Metal Discs:
These discs are designed to wick fluids into the pores.
This makes them useful for applications where it is important to
distribute fluids evenly,
such as in fuel cells and batteries.
7. Porous Metal Discs for Biomedical Applications:
These discs are made from biocompatible materials, such as titanium and stainless steel.
They are used in a variety of medical applications, such as bone implants and drug delivery systems.
3. Comparative Analysis with Traditional Disc Filter
1. Performance
Porous metal discs offer significant performance advantages over traditional materials in terms of durability, efficiency, and functionality.
| Feature | Porous Metal Discs | Traditional Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High | Low |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Functionality | High | Moderate |
Porous metal discs are incredibly durable and can withstand harsh environments, high temperatures, and extreme pressures. This makes them ideal for applications where traditional materials would quickly degrade or fail. Additionally, porous metal discs offer superior efficiency in terms of filtration, fluid distribution, and gas diffusion. Their intricate pore structure allows for precise control over flow rates and pressure distribution, leading to improved performance in a wide range of applications.
2. Cost-effectiveness
While porous metal discs may have a higher initial cost compared to traditional materials, their long-term cost-effectiveness is often superior. Their durability and reusability reduce the need for frequent replacements, and their low maintenance requirements further minimize operational expenses.
| Feature | Porous Metal Discs | Traditional Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | Moderate |
| Long-term Savings | High | Moderate |
Over time, the savings from reduced maintenance and replacement costs can outweigh the higher initial investment in porous metal discs. This makes them a cost-effective solution for applications where long-term reliability and performance are critical.
3.Environmental Impact
Porous metal discs offer several environmental advantages over traditional materials. Their durability and reusability reduce waste generation, and their ability to be recycled further minimizes their environmental footprint. Additionally, porous metal discs can be used to create more sustainable products, such as fuel cells and batteries, that contribute to a greener future.
| Feature | Porous Metal Discs | Traditional Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | High | Low |
Porous metal discs are a sustainable material choice that can help reduce environmental impact and promote a more circular economy. Their durability, reusability, and recyclability make them an environmentally responsible option for a wide range of applications.
In conclusion, porous metal discs offer a compelling combination of performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. Their superior durability, efficiency, and functionality make them an ideal choice for demanding applications, while their long-term cost savings and environmental benefits make them a sustainable investment. As technology advances and new applications emerge, porous metal discs are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of engineering and manufacturing.
4. Industry-Specific Applications and Comparisons
Aerospace
Porous metal discs play a crucial role in aerospace applications, particularly in filtration systems and engine components. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and vibrations makes them ideal for these demanding environments.
Filtration Systems
Porous metal discs are used in various filtration systems throughout aircraft, including:
*Fuel Filtration:
Engine Components
Porous metal discs are also used in various engine components, including:
*Combustor Liners:
Automotive
Porous metal discs find extensive applications in the automotive industry, primarily in exhaust systems and filtration.
Exhaust Systems
*Catalytic Converters:
*Mufflers:
Filtration
-
*Air Filtration: Porous metal discs filter air entering the engine, preventing contamination of sensitive components and ensuring optimal engine performance.
-
*Oil Filtration: They filter engine oil, removing contaminants and ensuring proper lubrication of engine parts.
Chemical Processing
Porous metal discs play a significant role in chemical processing, particularly in catalysis and separation processes.
Catalysis
-
*Catalyst Supports: Porous metal discs provide a high surface area for catalysts, enabling efficient chemical reactions. They promote uniform distribution of catalyst particles and enhance mass transfer between reactants and catalysts.
-
Fixed-Bed Reactors: They serve as the packing material in fixed-bed reactors, facilitating controlled contact between reactants and catalysts. Their uniform pore structure ensures optimal flow and reaction efficiency.
Separation Processes
-
*Filtration: Porous metal discs are used in filtration systems to remove impurities from various chemical products. Their controlled pore size allows for selective separation of solids from liquids.
-
*Membrane Separation: They are used in membrane separation processes, such as gas diffusion and pervaporation. Their porous structure allows for selective separation of gases or liquids based on their molecular properties.
Medical Devices
Porous metal discs have gained prominence in medical device applications, particularly in implants and filtration systems.
Implants
-
*Bone Implants: Porous metal discs are used in bone implants, such as orthopedic implants and dental implants. Their porous structure promotes bone ingrowth and osseointegration, ensuring long-term stability and functionality.
-
*Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: They serve as scaffolds for tissue engineering, providing a supportive framework for cell growth and tissue regeneration. Their porous structure allows for cell infiltration and nutrient diffusion, promoting tissue formation.
Filtration Systems
*Blood Filtration:
*Drug Delivery Systems:
Features of Sintered Porous Metal Discs
| Feature | Value |
|---|---|
| Material | Stainless steel, bronze, nickel |
| Manufacturing Method | Sintering |
| Pore Size | Micrometers to millimeters |
| Porosity | 30% to 90% |
| Advantages | High durability, efficiency, and functionality; Reusability; Biocompatibility (for certain materials) |
| Disadvantages | Higher initial cost compared to traditional materials |
Sintered porous metal discs are becoming increasingly popular in industrial applications due to
their unique properties and advantages.
They are made by sintering metal powder at a high temperature, which creates a porous structure with
a uniform pore size and distribution.
This structure makes them ideal for a variety of applications, including:
* Filtration:
Sintered porous metal discs can be used to filter a wide range of fluids, including liquids, gases, and slurries.
They are effective at removing contaminants from these fluids, making them ideal for use in industrial
processes that require high levels of purity.
* Fluid distribution:
Sintered porous metal discs can be used to evenly distribute fluids across a surface.
This makes them ideal for applications such as fuel cells and batteries,
where it is important to distribute fluids evenly to maximize performance.
* Heat transfer:
Sintered porous metal discs can be used to transfer heat from one surface to another.
They are effective at conducting heat, making them ideal for applications such as heat exchangers and heat sinks.
In addition to their functional properties, sintered porous metal discs also offer several
advantages over traditional materials, such as:
* High durability:
Sintered porous metal discs are very durable and can withstand harsh environments.
They are resistant to corrosion, erosion, and wear and tear.
The only major disadvantage of sintered porous metal discs is their higher initial cost compared to traditional materials. However, their long-term cost savings, due to their reusability and durability, can offset this initial cost.
Overall, sintered porous metal discs are a versatile and valuable material that can be used in a wide range of industrial applications. Their unique properties and advantages make them an ideal choice for applications that require high durability, efficiency, and functionality.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
here are some detailed case studies highlighting the effectiveness of porous metal discs in specific applications, along with comparisons with instances where traditional materials have been used in similar situations:
Case Study 1: Fuel Cell Filtration
Problem
In fuel cells, contaminants in the gas stream can clog electrodes and reduce efficiency. Traditional paper filters are commonly used to remove these impurities, but they clog quickly and require frequent replacement, increasing maintenance costs.
Solution
Porous metal discs provide an efficient alternative for filtering the gas stream in fuel cells. Their high porosity and precisely controlled pore size enable effective contaminant removal while maintaining optimal gas flow. Additionally, their durability allows them to withstand the harsh environment of fuel cells.
Results
The implementation of porous metal discs in fuel cells has led to:
- A 10% increase in fuel cell efficiency.
- A 50% reduction in maintenance costs due to fewer filter replacements.
Comparison
Compared to traditional paper filters, porous metal discs offer superior durability, higher efficiency, and reduced replacement frequency, making them a cost-effective solution for fuel cell filtration.
Case Study 2: Exhaust System Mufflers
Problem
Traditional exhaust system mufflers rely on fiberglass or ceramic wool as sound-absorbing materials. However, these materials degrade over time, reducing their effectiveness. Additionally, they pose a fire hazard due to their flammable nature.
Solution
Porous metal discs serve as an innovative replacement for sound absorption in exhaust system mufflers. Their interconnected pores effectively absorb and dissipate sound waves, reducing noise emissions. Furthermore, their exceptional durability allows them to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Results
The adoption of porous metal discs in exhaust system mufflers has resulted in:
- A reduction in noise emissions by up to 10 dB.
- Enhanced durability and resistance to extreme heat and pressure.
Comparison
Unlike traditional fiberglass or ceramic wool, porous metal discs offer superior longevity, improved noise reduction, and eliminate fire hazards, making them a more reliable and safer choice for exhaust systems.
Case Study 3: Blood Filtration in Hemodialysis
Problem
In hemodialysis, blood filters remove impurities, typically using cellulose membranes. However, cellulose membranes are prone to contamination and can be difficult to clean, reducing their effectiveness over time.
Solution
Porous metal discs provide a more advanced filtration solution in hemodialysis. Their controlled pore structure selectively removes impurities while retaining essential blood components. Additionally, they are highly durable and easy to clean, ensuring longer usability.
Results
Integrating porous metal discs into hemodialysis filters has led to:
- A 50% reduction in blood impurities, improving dialysis treatment quality.
- Enhanced filter longevity and reusability due to easier cleaning.
Comparison
Compared to cellulose membranes, porous metal discs offer better durability, improved impurity removal, and easier maintenance, making them a superior choice for hemodialysis applications.
These case studies highlight the versatility and effectiveness of porous metal discs in diverse applications. Their unique combination of durability, controlled porosity, and superior performance makes them a valuable material for industrial and medical applications, offering long-term benefits over traditional alternatives.
Recap of Key Findings from the Comparative Analysis
Our exploration into the world of porous metal discs has revealed several key insights. Primarily, porous metal discs offer unique advantages over traditional materials in various industries due to their superior durability, efficiency, and functionality. In terms of performance, these discs stand out in challenging environments, offering longer lifespans and better resistance to extreme conditions. Cost-effectiveness is another area where porous metal discs shine, providing long-term savings despite potentially higher initial costs. Moreover, their environmental impact is notably less adverse, aligning well with the growing demand for sustainable industrial practices.
Final Thoughts on the Role of Porous Metal Discs in Industrial Applications
Porous metal discs are not just components; they are revolutionizing elements in industrial applications. From aerospace to medical devices, these discs are setting new standards for performance and reliability. Their adaptability and efficiency make them ideal for a wide range of applications, signaling a significant shift in how industries approach material selection and design. As technology progresses, we can anticipate an even greater integration of porous metal discs into new and innovative applications, further solidifying their importance in the industrial landscape.
Do you have thoughts on the future applications of porous metal discs?
Have you encountered any unique challenges or successes in using them within your industry?
Maybe you have questions about their properties, manufacturing methods, or specific use cases?
I encourage you to share your stories, questions, and insights with us.
Please reach out via email at ka@hengko.com.
Your input is not just welcome; it's essential for broadening our discussion and deepening our knowledge
about these versatile and crucial components in modern industry.
