10 Questions of Industrial Humidity Sensor You Should Know
Humidity sensors play a critical role in many industrial applications, and understanding their capabilities and performance is important for ensuring optimal conditions in production, storage, and other processes. In this article, we will answer 10 frequently asked questions about Industrial Humidity Sensors.
1. What is an Industrial Humidity Sensor?
In short, An industrial humidity sensor is an electronic device that measures the humidity or moisture level in the air. It is commonly used in industrial settings to monitor the humidity levels in manufacturing and testing processes and in environments where humidity control is critical, such as storage facilities, clean rooms, and data centers. The sensor typically uses a capacitive or resistive element to measure the relative humidity and outputs a signal proportional to the level of humidity detected.
Are you familiar with the impact of humidity on industrial processes? While temperature control is commonly understood, humidity plays an equally critical role. Excess moisture can spoil food products, while too little humidity can damage electronics. Industrial humidity sensors exist to measure and detect humidity levels accurately, ensuring that environmental conditions are optimal for safe and high-quality production. This blog post will look in-depth at industrial humidity sensors, including their functions, types, and applications.
2. Why Industrial Humidity Control Is Crucial
Humidity can have a significant impact on various industrial processes and applications. For example, in pharmaceutical manufacturing, the humidity level can affect the efficacy and shelf-life of medicines and the risk of microbial growth. In the food processing industry, excess moisture in the ambient air can promote spoilage, decrease product quality, and even pose health hazards. In electronics manufacturing, high humidity levels can cause corrosion, oxidation, and static discharge, leading to component failure and reduced reliability. Therefore, controlling humidity levels is critical to ensuring consistent and high-quality outputs.
3. Types of Industrial Humidity Sensors
Several industrial humidity sensors are available, each with its own characteristics, advantages, and limitations. Here are some of the most commonly used types:
1. Capacitive Humidity Sensors
Capacitive humidity sensors are the most widely used type of industrial humidity sensors. They work on the principle of changes in the electrical capacitance of a polymer or ceramic material due to water molecules' absorption or desorption. As the humidity level changes, the dielectric constant of the sensing element changes, affecting the capacitance that can then be correlated to the surrounding air or gas's relative humidity (RH) level.
One of the advantages of capacitive humidity sensors is that they are highly accurate and easy to calibrate. They can also respond quickly to changes in humidity levels and require minimal maintenance. However, they may be affected by temperature changes, drift over time, and can be susceptible to contamination, especially in harsh industrial environments.
2. Resistive Humidity Sensors
Resistive humidity sensors, or hygroscopic, use a hygroscopic material such as lithium chloride or calcium chloride that absorbs moisture from the air. As the moisture content changes, the material's electrical resistance also changes, which can be detected and used to calculate the RH level.
Resistive humidity sensors are simple, low-cost, and can be used in various applications. However, they tend to be less accurate and respond slower than capacitive sensors, and the hygroscopic chemicals can dry out or degrade over time.
3. Optical Humidity Sensors
Optical humidity sensors use light-scattering or refractive index changes to measure humidity levels accurately. They work by emitting a light beam into the air or gas, then detecting the changes in the light beam's path, intensity, or frequency when water molecules are present. Optical humidity sensors are highly precise, fast, and reliable. Also, they are not affected by contaminants or cross-sensitivity issues. However, they tend to be more expensive, sensitive to temperature changes and require careful calibration.
4. Other Types of Humidity Sensors
Other industrial humidity sensors include resistive, capacitive, chilled mirrors, and dewpoint. These sensors may be suitable for specific industrial applications that demand high precision, stability, or durability.
4. How Industrial Humidity Sensors Work
Regardless of the type of sensor, industrial humidity sensors all work on the same basic principle of detecting the changes in the amount of water vapor present in the air or gas. The sensors convert these changes into an electrical signal that can be measured, displayed, and used for control or alarms. Here's a step-by-step guide on how industrial humidity sensors work:
Step 1: Sensing Element - The sensing element is the critical component of the humidity sensor that interacts with the surrounding air or gas. The element can be a polymer film, a ceramic plate, a hygroscopic material, or a combination of different materials based on the sensor type.
Step 2: Capacitance, Resistance, or Optical Signal - The sensing element converts the changes in humidity levels into electrical signals, either by changing the capacitance, resistance, or optical properties of the material.
Step 3: Signal Processing - The electrical signal is processed and transformed by the humidity sensor's electronics, typically to provide an output of relative humidity (RH) or absolute humidity (AH), temperature, or dew point.
Step 4: Calibration and Adjustment - The humidity sensor calibration process ensures that the output signal corresponds to the correct humidity level. Calibration may involve exposing the sensor to a known humidity source and adjusting the sensor's gain or offset until the output matches the expected value.
Step 5: Integration with the System - The humidity sensor output can be integrated into the overall control or monitoring system, which may involve a feedback loop, alarms, or automatic actions based on the measured humidity level.
5. Main Features of the industrial humidity sensor and Benefits?
The main features of an industrial humidity sensor include the following:
1. Accuracy: The sensor's accuracy is typically specified as a percentage of the actual value.
2. Range: The range of the sensor specifies how much humidity it can detect, usually expressed as a percentage of relative humidity.
3. Stability: The stability of the sensor refers to its ability to maintain accurate readings over time.
4. Output signal: The humidity sensor typically outputs its readings in the form of an analog voltage or current signal, or digital signal.
The benefits of an industrial humidity sensor include the following:
1. Improved product quality control: With accurate humidity monitoring, production processes can be optimized for better product quality control.
2. Energy savings: Humidity sensors can help regulate air conditioning and heating systems, leading to energy savings.
3. Mold and bacteria control: Maintaining proper humidity levels can help prevent mold and bacteria growth in manufacturing and storage facilities, making for a safer and healthier environment.
4. Reduced material waste: Monitoring humidity levels during manufacturing processes minimizes material waste due to moisture damage.
6. What are the popular industrial humidity sensors in the market now?
There are many types of industrial humidity sensors available in the market. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
1. Industrial temperature and humidity meter:
This type of sensor is typically used in industrial or laboratory settings to measure both temperature and humidity in the air. These meters are handheld devices that are easy to use, and they are often equipped with a digital display to show real-time readings. Industrial temperature and humidity meters are useful for quality control as they can help optimize production processes and ensure products are manufactured to the required specifications.
2. Industrial humidity transmitter:
Industrial humidity transmitters are often used in large industrial applications where monitoring of humidity levels is critical. These devices are designed to measure humidity levels and transmit the data wirelessly to a monitoring system. By using industrial humidity transmitters, facility managers can remotely monitor humidity levels and take action to regulate conditions if necessary. This ability to monitor humidity levels in real time can help prevent costly damage to products and equipment.
3. Industrial temperature and humidity sensor:
Industrial temperature and humidity sensors are often used in industrial settings to measure both temperature and humidity in the air. They are typically accurate, reliable, and easy to install, and they can be interfaced with a range of devices, such as data loggers and control systems. These sensors are used in various industrial settings, including manufacturing, HVAC, and clean rooms.
4. Industrial soil moisture sensor:
These sensors are used in agriculture and landscaping to measure the moisture content in the soil. They can help farmers and landscapers manage irrigation systems more efficiently by providing real-time feedback on soil moisture levels. Industrial soil moisture sensors can help prevent over-watering, leading to soil erosion and other environmental concerns.
5. Automotive humidity sensor:
Automotive humidity sensors are used in vehicles to monitor the humidity levels in the cabin air. These sensors are essential for maintaining the comfort of passengers as they can ensure that the air conditioning system is working properly. In addition, automotive humidity sensors can also help prevent mold and bacteria growth in the cabin air, creating a safer and healthier environment for passengers.
6. HVAC humidity meter:
This type of sensor is specifically designed for use in HVAC systems to measure humidity levels in the air. HVAC humidity meters can help optimize the performance of the HVAC system, improving energy efficiency and reducing operating costs. They are also important for ensuring occupants' comfortable and healthy environment by controlling humidity levels within the recommended range.
In conclusion, there are various types of industrial humidity sensors, each designed to meet specific application requirements. These sensors are essential in maintaining optimal conditions for production, storage, transportation, and other processes where controlling humidity levels is critical.
7. What is the Difference Industrial Humidity Sensor and with Normal Humidity Sensor?
The main difference between an industrial humidity sensor and a normal humidity sensor is the environment in which they are used. Industrial humidity sensors are designed to be used in industrial settings, where the conditions may be harsher and more demanding than in residential or commercial settings. Industrial humidity sensors are built to withstand moisture, dust, vibrations, and other factors affecting their performance.
Here are some of the other key differences between industrial and normal humidity sensors:
1. Accuracy and range: Industrial humidity sensors are often more accurate and have a wider measurement range than consumer-grade sensors. And also because they need to be able to measure a wider range of humidity levels with greater precision, depending on the application's requirements.
2. Calibration and maintenance: Industrial humidity sensors must be calibrated and maintained more frequently than normal humidity sensors to ensure their accuracy and performance over time. Regular calibration and maintenance are critical for ensuring sensor readings' reliability.
3. Output signal: Industrial humidity sensors typically output signals in the form of an analog voltage or current signal, or digital signal, while consumer-grade sensors may have a simpler output, such as a basic display.
4. Specialized features: Industrial humidity sensors may have specialized features such as operating in high temperatures or humid environments, built-in data logging functionality, or a transmitter that sends data to a monitoring system.
In conclusion, industrial humidity sensors are designed to meet the specific needs of industrial applications and are built to withstand the harsher conditions that may be encountered in these environments. While consumer-grade humidity sensors may be suitable for basic applications, industrial humidity sensors are essential for maintaining optimal conditions and ensuring accuracy and reliability.
8. What are the Product structure and main components of industrial temperature and humidity sensors?
The product structure of an industrial temperature and humidity sensor can vary depending on the design and manufacturer. Still, generally, most sensors consist of three main components: a sensor element, a measurement circuit, and a housing.
1. Sensor element: The sensor element is the part of the sensor that directly detects the relative humidity and temperature of the surrounding environment. The most commonly used type of sensor element in these sensors is a capacitive humidity sensor, which consists of a thin polymer film that changes capacitance as it absorbs or releases water vapor. The element also contains a thermistor or other temperature sensor to detect changes.
2. Measurement circuit: The measurement circuit reads the signals from the sensor element and converts the data into a digital or analog output that a computer or other device can read. This circuit is typically integrated into a microcontroller or other measurement board for interfacing with measuring equipment or process control systems.
3. Housing: The Humidity Sensor housing is the outer casing of the sensor that protects the internal components from damage and provides a mounting mechanism to secure the sensor in place. The housing is designed to resist any environmental conditions, such as moisture, dust, and electromagnetic interference.
4. Probe: Humidity Sensor Probe is a type of sensor that measures the relative humidity in the air using a sensing element and a probe wire or casing. The sensing element is embedded in the probe head and detects changes in humidity levels in the surrounding environment. The probe wire or casing is a protective cover for the sensing element that helps to shield it from moisture and other environmental factors that may affect its accuracy or performance.
Humidity sensor probes can be used in a range of applications, including HVAC systems, food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and clean rooms. They are typically designed to be rugged and durable, so they can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including high humidity levels, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to chemicals or other contaminants.
There are many different types of humidity sensor probes available, including capacitive, resistive, and optical sensors. The type of probe used depends on the specific application requirements, such as accuracy, sensitivity, response time, and other factors. Proper calibration and routine maintenance are important for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of humidity sensor probes over time.
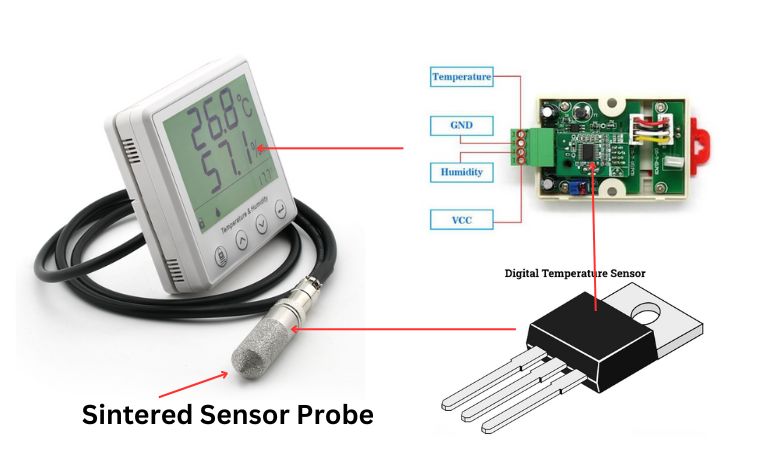
When these components are assembled, the Industrial Temperature and Humidity Sensor can accurately and reliably measure the relative humidity and temperature, making it useful in various industrial applications, including manufacturing, HVAC, and clean rooms.
9. Applications of Industrial Humidity Sensors
Industrial humidity sensors can be used in various applications and industries, including:
HVAC Systems
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are used in buildings and facilities to regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality. Industrial humidity sensors can be integrated into HVAC systems to ensure optimal comfort and safety for occupants and prevent mold growth, condensation, and equipment damage.
Data Centers
Data centers are critical infrastructures that require stable and controlled environments to ensure the efficacy of servers, storage, and networking devices. Industrial humidity sensors can be used to monitor humidity levels, affecting IT equipment's performance and reliability, especially in high-density computing environments.
Food Processing
Food processing and storage require strict humidity control to prevent spoilage, preserve quality, and ensure compliance with food safety regulations. Industrial humidity sensors can detect excess moisture levels in the air or packaging and trigger alarms or automatic systems for dehumidification or ventilation.
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical manufacturing must follow strict guidelines and quality assurance standards to ensure medicines' efficacy, stability, and safety. Humidity control is a vital aspect of pharmaceutical manufacturing, affecting drug stability, solubility, and bioavailability. To prevent moisture buildup and microbial contamination, industrial humidity sensors can normally monitor critical areas such as sterile manufacturing rooms, drying chambers, and packaging rooms.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing industries such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive require precise humidity control to ensure consistent product quality and safety. Industrial humidity sensors can prevent static discharge, corrosion, and degradation of materials, components, and products.
10. Other FAQs about Industrial Humidity Sensor
1. What is the range of humidity that Industrial Humidity Sensors can measure?
Answer: The range of humidity that Industrial Humidity Sensors can measure varies depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. However, most Industrial Humidity Sensors can typically measure humidity levels between 0-100% relative humidity (RH).
2. What is the accuracy specification of Industrial Humidity Sensors?
Answer: The accuracy specification of Industrial Humidity Sensors varies depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. However, accuracy specifications are typically expressed as a percentage of the actual value and can range from ±1% RH to ±5% RH.
3. What are the output options for Industrial Humidity Sensors?
Answer: The output options for Industrial Humidity Sensors typically include analog voltage or current signals, digital signals like RS-232 or RS-485, or pulse outputs. The type of output depends on the specific model and application requirements.
4. Can Industrial Humidity Sensors be calibrated or adjusted?
Answer: Many Industrial Humidity Sensors can be calibrated or adjusted to ensure accuracy and performance over time. Calibration procedures involve exposing the sensors to a controlled environment with a known humidity level to verify their readings and make adjustments if necessary.
5. How long do Industrial Humidity Sensors last?
Answer: The lifespan of Industrial Humidity Sensors depends on various factors, including the specific model, operating environment, and maintenance schedule. However, many Industrial Humidity Sensors can last several years with proper care and maintenance.
6. What is the response time of Industrial Humidity Sensors?
Answer: The response time of Industrial Humidity Sensors varies depending on the specific model and application requirements. However, many sensors have a 10-15 seconds response time.
7. How do Industrial Humidity Sensors compare to other types of humidity sensors?
Answer: Industrial Humidity Sensors are often more accurate and reliable than consumer-grade humidity sensors due to the demanding environments they are designed to operate in. They are also built to withstand harsh conditions and more rigorous testing procedures than consumer-grade sensors.
8. What types of Industrial Humidity Sensors are available?
Answer: There are many types of Industrial Humidity Sensors available, including capacitive, resistive, dew point, and chilled mirror sensors. The specific type of sensor depends on the application requirements, environmental conditions, and other factors.
9. How do I choose the right Industrial Humidity Sensor for my application?
Answer: Choosing the right Industrial Humidity Sensor depends on various factors, including the desired accuracy and range, the specific application requirements, and the environmental conditions. Working with a knowledgeable supplier or manufacturer can help you select the right sensor for your needs.
10. How do I install and maintain Industrial Humidity Sensors?
Answer: Installation and maintenance procedures vary depending on the specific model and application requirements but typically involve following manufacturer guidelines for mounting, wiring, and calibrating the sensor. Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring accurate readings and preventing sensor damage.
If you're looking for quality Industrial Humidity Sensors, HENGKO can offer you a wide range of options to meet your needs.
Our sensors are built to withstand tough industrial conditions and provide accurate and reliable readings.
Don't hesitate to contact us at ka@hengko.com to learn more about our range of industrial sensors and how we can help you meet your requirements.
Send your message to us:
